Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of Enterprise Service Management, the careful implementation of ServiceNow’s Hardware Asset Management (HAM) is pivotal for achieving organizational efficiency and compliance. This blog will guide IT asset managers through a structured journey, emphasizing the importance of strategic assessment, data reconciliation, environment preparation, ongoing data reconciliation, configuration of Install, Move, Add, Change and Decommission (IMACD) processes, and continuous service improvement.
Objectives:
The objectives of the HAM process are to:
- Ensure all hardware assets are recorded and maintained in the asset repository.
- Accurately identify hardware assets to be refreshed or retired.
- Ensure all maintenance and contractual information is maintained in the asset repository and linked to appropriate asset records.
- Capture purchase order information from corporate procurement functions to enable the receipt of hardware assets and the initial creation of asset records.
- Ensure efficient tracking of hardware asset details resulting from Configuration Item (CI) installation, moves, additions, changes, or replacements.
- Provide prompt registration and updates of hardware asset records to enable the performance of other service management processes (e.g. recording of asset records prior to the implementation of a Physical CI, data feeds into charge/showback processes).
Customer Business Value:
- Increases consistency in the execution of HAM processes with standard processes.
- The integrated HAM process connects stockroom, procurement, and field services activities. This synergy enables continuous accuracy in the asset repository, informed by data from asset-related transactions. It also fosters efficient utilization of existing inventory, preventing unnecessary purchases.
- Avoids penalties and derives the maximum benefits from maintenance and lease contracts.
- Provides accurate hardware asset data to make informed business decisions about ongoing and future investments.
- Provides accurate reports to Asset Owners in accordance with audit requirements.
Implementation Journey Guide:
The implementation of HAM requires the creation of a one-time asset inventory and the establishment of the Asset Life Cycle Management process. Our journey unfolds in a series of strategic steps, each designed to seamlessly lead us toward successful HAM implementation – from the initial strategic assessment of data sources, evaluating their capability and relevance, to the continuous cycle of monitoring and improvement. This guide is more than a roadmap; it’s a narrative, outlining the practical steps that bridge process objectives and customer business value, adopting a culture of continuous enhancement. More importantly, each solution presented here is adaptable based on specific organizational use cases, ensuring a tailored approach that aligns precisely with the unique needs and challenges of your environment.
Use Cases and Solutions
Use Case 1: Lack of Visibility into Deployed Assets
- Solution: Recognized as a priority 1 challenge, this requires immediate attention. Execute the implementation Steps 1 to 3, mentioned below, to develop a reliable and real-time view of deployed assets, forming the foundational stage of our implementation journey.
Use Case 2: Lack of Consistency and Reliability in Real-time Data
- Solution: If organizations have implemented Use Case 1 but have issues with data consistency, this transforms into a priority 2 concern. Improve it by undertaking Implementation Step 4, emphasizing the automation of continuous data imports from diverse sources to maintain and scrutinize real-time data for well-informed decision-making.
Use Case 3: Manual and Time-Consuming Hardware Purchase Requisitions
- Solution: As a priority 3 challenge, address it by executing Step 5, i.e., configuring the service request process for management IMACD and automate the other processes in streamlining and expediting the requisition process, fostering efficiency.
Step by Step Implementation Guide:
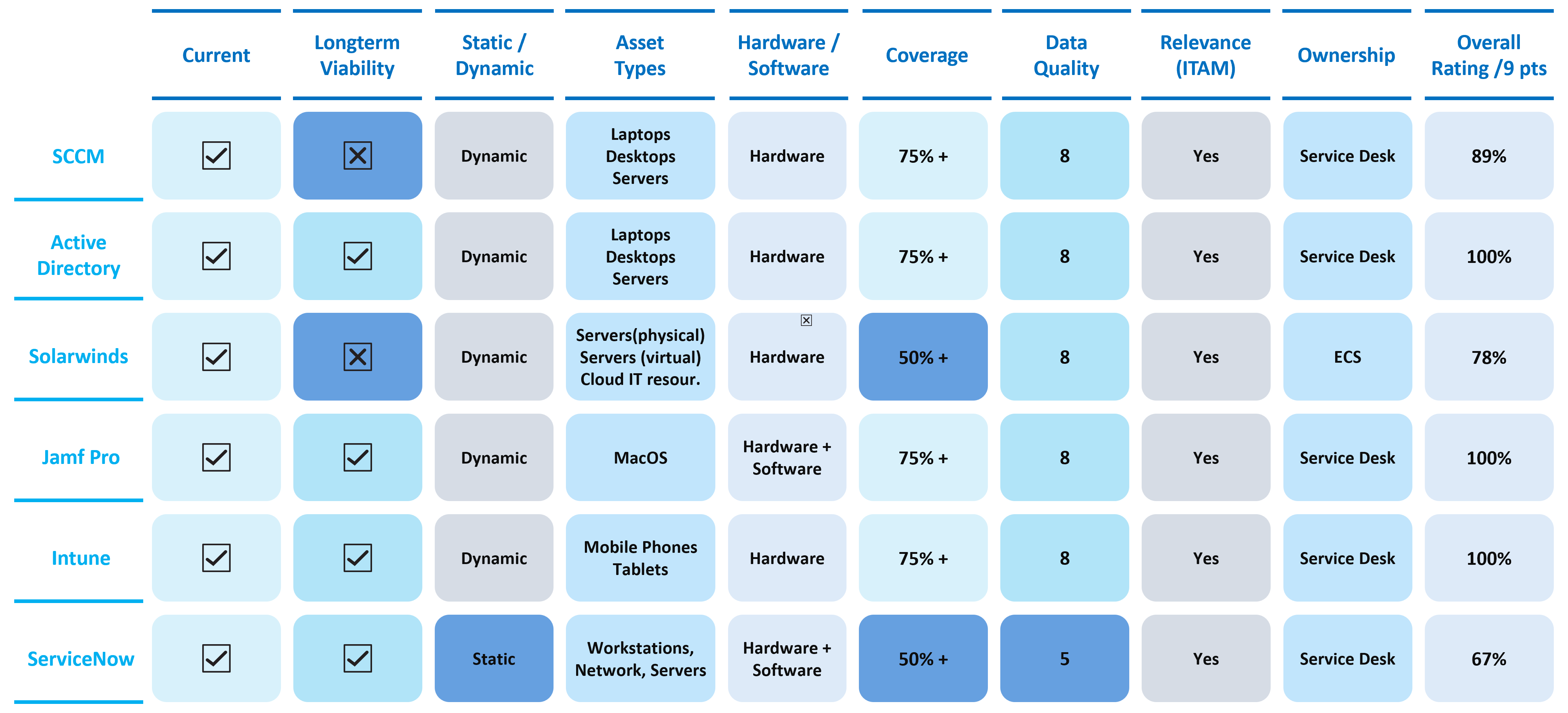
Step 1: Strategic Assessment of Data Sources: Conduct in-depth analysis of the IT landscape and stakeholders discussions to evaluate data sources, assess their nature, scrutinize asset coverage types, and determine data quality for both current and future-proofing needs. A comprehensive decision-making framework is established by evaluating the following nine critical criteria, which offers a holistic perspective for informed choices.
- Current Status: Scrutinize if the data source is presently deployed, operational, or in inactive use, and whether it is well-maintained.
- Long-Term Viability: Ascertain the future-proofing of the data source, evaluating its commitment to the organization for a minimum of two years.
- Dynamic or Static Nature: Investigate whether the data source is dynamically maintained or utilized as a one-off snapshot. Static sources may be employed for a single import, while dynamic sources involve ongoing updates through APIs.
- Asset Types: Identify the array of asset types covered by the data source to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Hardware and Software Inclusion: Determine if the data source encapsulates information about hardware only, or if it extends to cover both hardware and software.
- Extent of Coverage: Measure the reach of the data source across the organization’s IT estate, represented as a percentage derived from feedback in one-to-one meetings.
- Data Quality Assessment: Subjectively rate the perceived data quality based on feedback gathered during one-to-one meetings.
- Relevance in IT Asset Management (ITAM): Evaluate the relevance of the data source within the context of a mature Asset Management function.
- Ownership Identification: Pinpoint and document the known owner(s) of the data source within the organization.
Holistic Rating: Calculate the overall rating by summing up the points achieved for each data source rating. Assign one point for green cells, signifying compliance and reliability, and zero points for amber cells, indicating potential issues. Express the rating as a percentage of the total possible score across the nine criteria.
Step 2: Data Reconciliation for Golden Records: Establishing a reliable baseline is vital in preparing IT asset inventory. Perform this one-time activity based on the identified most reliable source of truth data sources. If there are multiple data sources for the same asset types, cross-reference and reconcile them to create golden records, ensuring accuracy and dependability. Overcoming data quality issues is vital as a part of this exercise for building a robust foundation for further implementation.
Step 3: Conduct One-Time Asset Import for Trustworthy Asset Management: Prepare the environment with foundational data and execute a one-time asset import. This involves reviewing and updating trustworthy data locations, cost centers, and departments, as well as defining asset taxonomy, stockrooms. Perform model normalization and content curation to address data quality issues.
Step 4: Ongoing Data Reconciliation through APIs and Discovery: Implement APIs and Automated Discovery for continuous updates. Ensure critical data like expiration dates and renewal reminders are captured. Enable automated alerts for contract expiries and use dashboards for clear contract status overviews. Identify integration requirements, integrate trusted data sources, and validate data against mandatory fields. Create test scripts to ensure ongoing data quality validation.
Step 5: Configure IMACD Process for Asset Management Life Cycle: Implementing the IMACD process is crucial for managing the asset management life cycle efficiently. Set up bundle services, configure the Asset IMACD life cycle, and automate processes such as shipping, label printing, sourcing, purchase, asset provisioning, and decommissioning. This step ensures a streamlined and automated asset management workflow.
Monitor and Continuously Improve Service
To ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the implemented system, configure Mobile Asset app for regular asset audits. Schedule and perform data certification, leverage out-of-the-box reports to review results, and take proactive actions. Identify and manage risks associated with compliance and financial aspects, fostering continuous service improvement.

“Effective Hardware Asset Management (HAM) aligns meticulously with organizational goals and compliance. It’s the backbone of operational efficiency, ensuring every asset is a strategic contributor to the enterprise’s growth. Our HAM journey, from strategic assessment to continuous improvement, embodies our commitment to precision and sustainability in asset lifecycle management.”
Naveen AMUDALAPELLI
Head of Enterprise Service Management
Conclusion:
This comprehensive guide provides IT Asset Managers with a structured approach to implement HAM successfully. Following these steps will not only establish a reliable asset management system but also contribute to the overall efficiency and compliance of the organization. As we navigate this journey, the implementation guide transforms into a narrative, bridging process objectives with tangible customer business value and fostering a culture of continuous enhancement.






